Problem
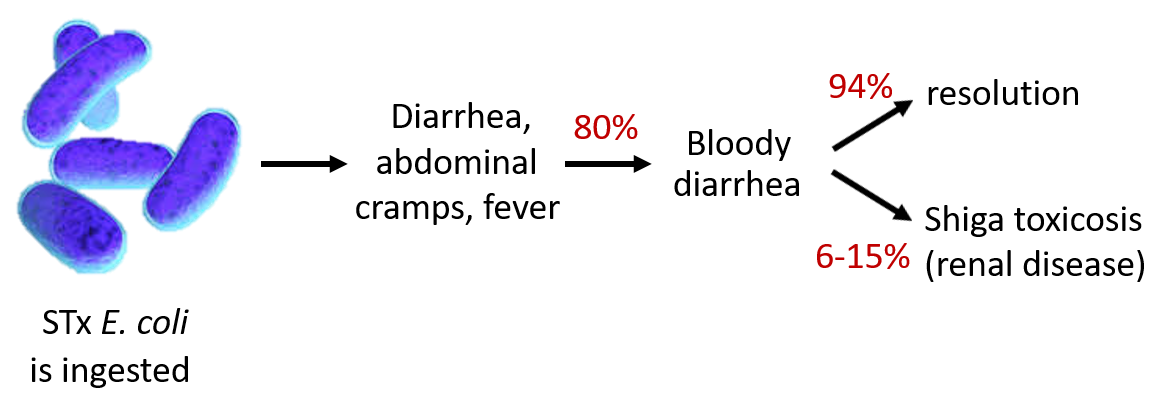
Over 100,000 people suffer from Shiga toxin-producing E. coli infections every year which cause gastrointestinal illness. In 5% to 15% of cases, these toxins enter the bloodstream, which can result in fatal renal disease. These infections are currently untreatable, as traditional antibiotics induce higher toxin concentrations and worsen illness. Currently, no therapies exist beyond attempts to mitigate symptoms. Blocking the way these toxins invade cells is an attractive therapeutic strategy for fighting these infections. Unfortunately, attempts to exploit this approach have fallen short as reported interventions are only effective against one toxin, STx1, while the other toxin, STx2, is 400x more lethal. Identification of drugs that can safely target both toxins remains a critical and unmet need.
Solution
The Mukhopadhyay Lab at The University of Texas at Austin has recently discovered that an off-patent drug used for breast cancer therapy, Tamoxifen, may also be valuable for treating these lethal E. coli infections. This drug works by increasing the pH of the cell which changes cellular dynamics and in turn blocks the transport of toxins to the cell. The toxins are then redirected and subsequently degraded by the cell, preventing harmful toxicity. Published in Life Science Alliance1, the researchers report that treatment with Tamoxifen resulted in significantly improved survival rates in mouse models infected with lethal doses of STx1 and STx2. This is the first proposed drug candidate that targets both Shiga toxins and enables broad use against lethal E. coli infections. Furthermore, Tamoxifen is already FDA-approved for human use, speeding up and simplifying clinical translation efforts. Repurposing this drug for treating lethal and previously untreatable E. coli infections holds tremendous promise for improving patient care and survival.
Reference
1. Selyunin, A.S., et al., Life Science Alliance 2, 3 (2019). https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.201900439

